Where Did the First Humans Really Come From?
Have you ever wondered? Earth originally had no humans, but where did we come from? When did the first man and woman emerge?
Four billion years ago, a sphere encased in dust and rock orbited through the vast expanse of space. Yes, it was Earth. Since its creation, the Earth's climate has fluctuated between cold and warm. Initially, Earth lacked oxygen, so life existed on Earth. But over the intervening centuries, shallow oceans, influenced by lunar tides, powered by volcanic heat and seeded by organic molecules from space, transformed chemical components into biological ones, giving rise to the first life on Earth.
The Birth of Humanity
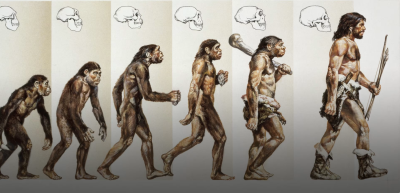
Human ancestors initially evolved an arboreal lifestyle to avoid the dinosaurs. Following the extinction of the dinosaurs in the Late Cretaceous, human ancestors continued this lifestyle in Africa. With the movement of tectonic plates, the Great Rift Valley formed, and climate change occurred in Africa, transforming the rainforest into a savannah. Our ancient ancestors also shifted their lifestyle, from living in the trees to terrestrial life, gradually evolving into primates. Over a 25 million-year period, these primates began evolving in two directions: one group became monkeys, while the other gradually evolved into humans. Six million years ago, one group slowly branched out into chimpanzees, resulting in chimpanzee DNA that is 99% similar to humans.
3.5 million years ago, African apes, pressured by survival, left the forests and entered the grasslands. To survive, these apes learned to walk upright and began to make tools necessary for daily life. Over time, their brains grew increasingly developed, and 2.49 million years ago, a new species, Homo habilis, emerged, capable of making simple tools and using simple language. This marked a significant historical moment in the emergence of humans.
As humans evolved, their body structure gradually changed. In addition to eating fruit, they also adopted a meat-based diet, which shortened their intestines. Meat, with its high energy and protein content, provided them with ample energy for the development of other organs, leading to the gradual expansion of their brain capacity and other organs.
Darwin's Speculation
In his 1871 book, The Descent of Man and Selection in Relation to Sex, Darwin first proposed the scientific hypothesis that humans originated in Africa. Based on his theory of evolution, he believed that Africa likely possessed the necessary conditions for the evolution of apes into humans.
Favorable Conditions in Africa
When Darwin hypothesized that Africa was the cradle of humanity, he emphasized the following favorable factors:
- Ape population: Africa possessed a large population of apes, providing the species foundation for evolution.
- Climate: Tropical and subtropical climates were conducive to the survival and reproduction of organisms.
- Resource abundance: A diverse array of plant and animal resources supported the needs of early humans.
Conclusion
The evolution from Australopithecus to modern civilization did not emerge suddenly, but rather evolved step by step over a long period of history. We do not need to trace whether our ancestors were male or female, let alone whether the first born was male or female, because scientists study populations, not individuals, and we cannot find the answer to this question.


